
Basic Chest X-RayInterpretation
Adam Guttentag, M.D.
© Copyright Adam Guttentag, MD
All Photos Retain the Copyrights of Their Original Authors

How do you look at achest x-ray?
Avoid tunnel vision!Avoid tunnel vision!
or



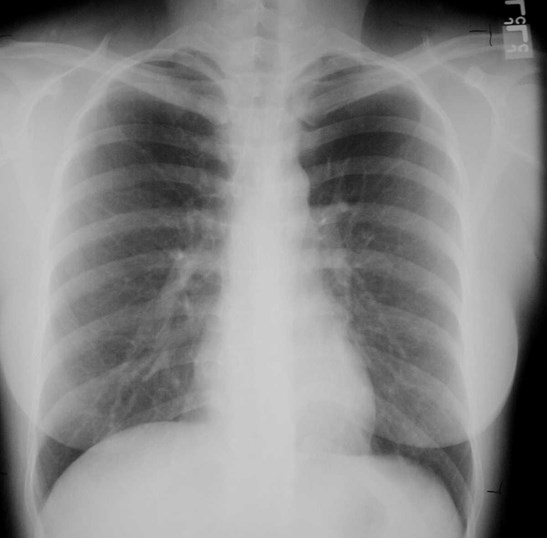

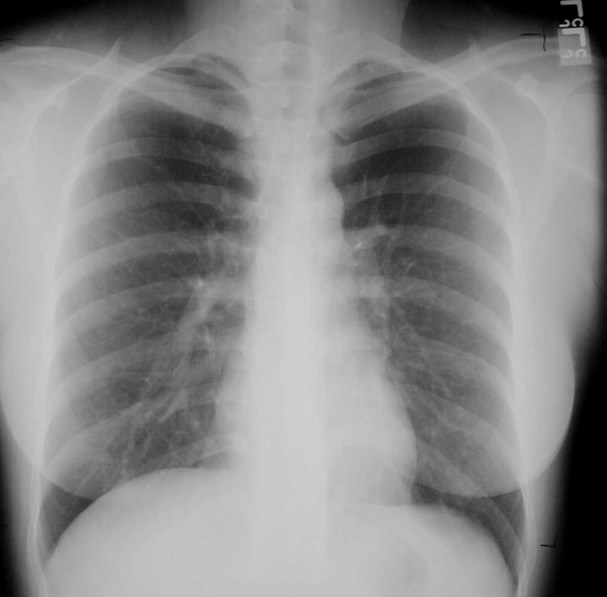


Chest wall, bones and abdomen





Mediastinum, heart and hila





Lungs

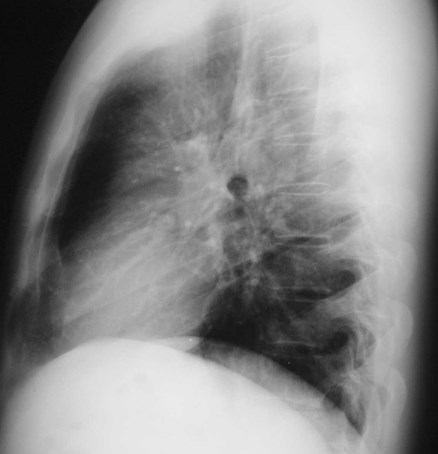
The Lateral Chest Film
•Find abnormalitieshidden on the frontalfilm
•Confirmabnormalitiessuspected fromfrontal film
•Don’t be afraid tolook at it!
Our best friend!

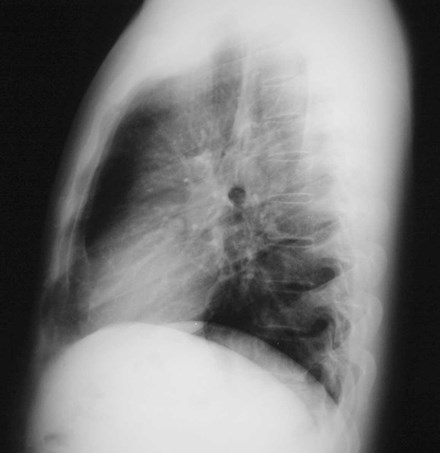
Looking at the lateral CXR

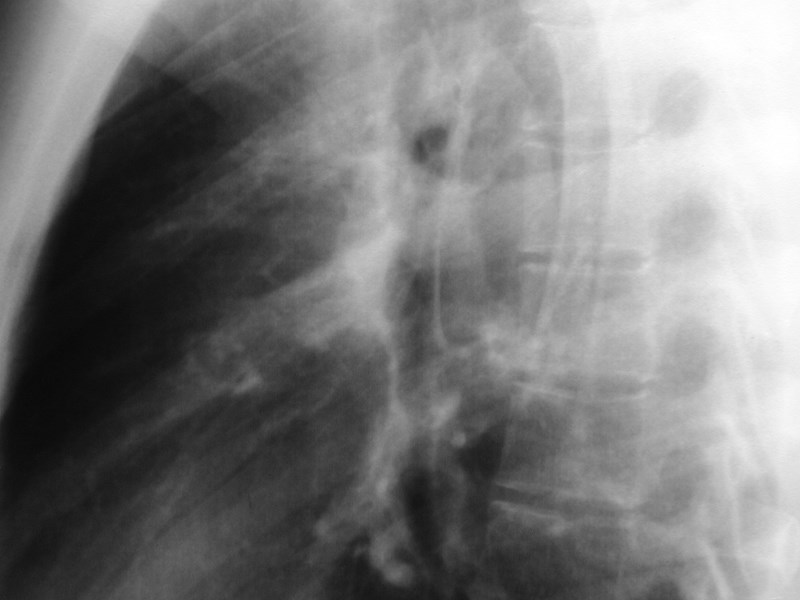

Hilar structures on the lateral film:

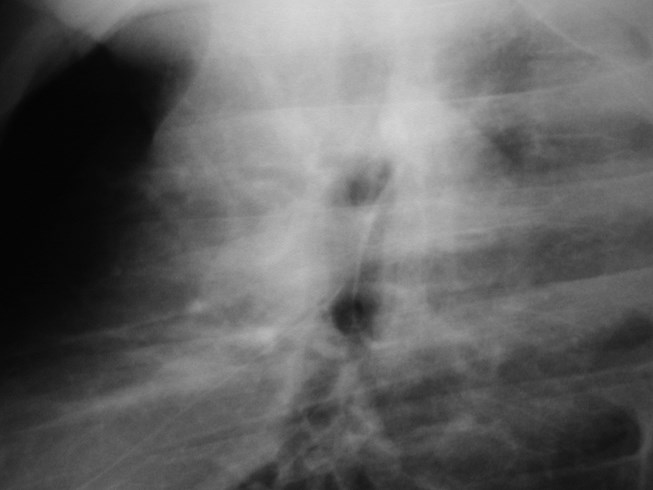

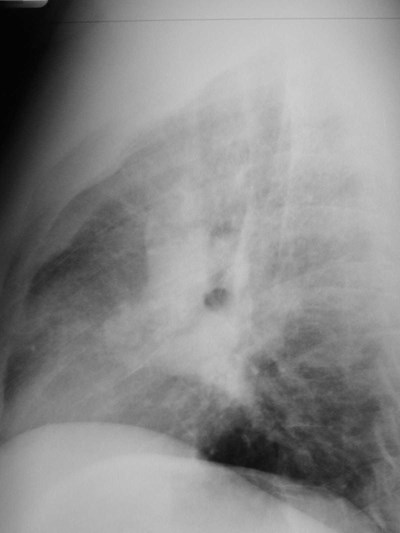
“Ring around thebronchus”

Technical Factors
•Positioning
straight vsoblique
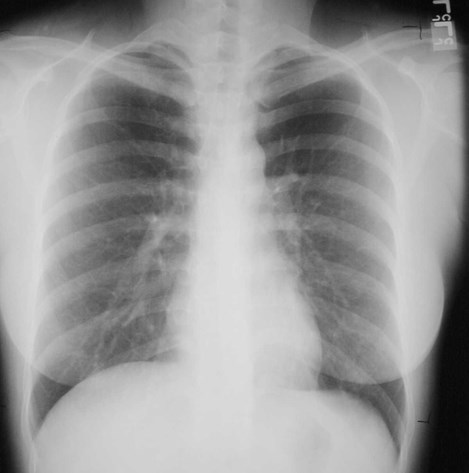
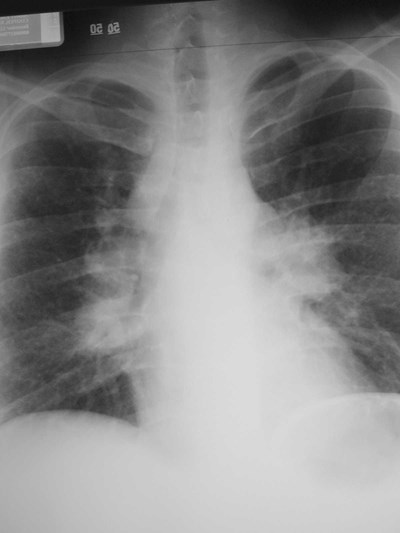
(How we’ll try to fool you)

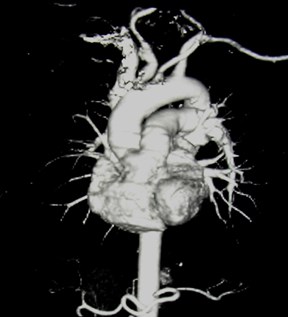
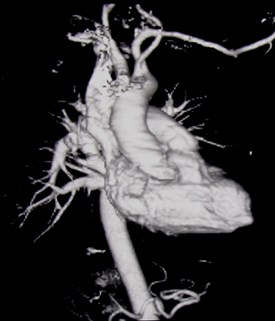
Effect of obliquity on heart size

Technical Factors
•Positioning
straightvs oblique
PA vs AP

Technical Factors
•Positioning
straight vsoblique
PA vs AP
erect vssupine
erect
supine

Technical Factors
•Positioning
straight vsoblique
PA vs AP
erect vs supine
lordotic vskyphotic
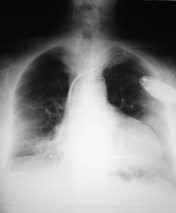
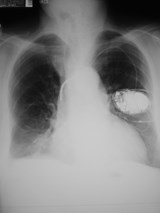
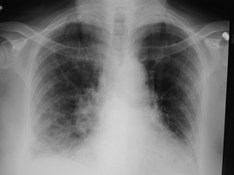
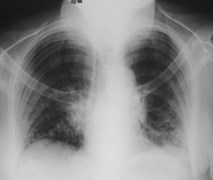
lordotic
kyphotic

Technical Factors
•Positioning
straight vsoblique
PA vs AP
erect vssupine
lordotic vskyphotic
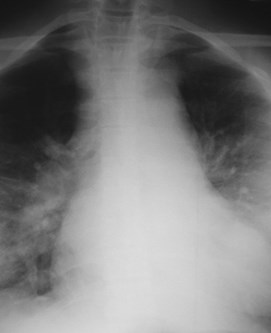
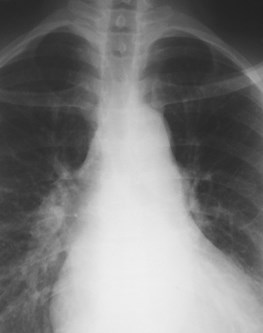
Effect on mediastinal contour

Technical Factors
•Depth of inspiration
•Visualization ofpathology depends oncontrast provided by airin the lungs
•Count ribs!
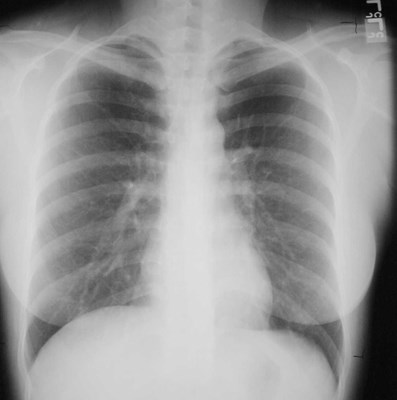
10

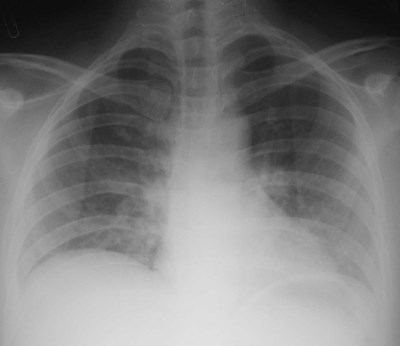
8
Short of breath
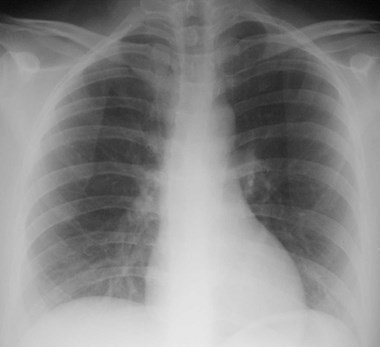
One minutelater
8

Technical Factors
Body habitus
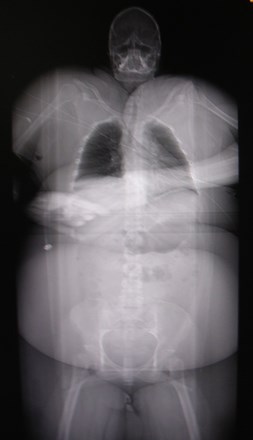
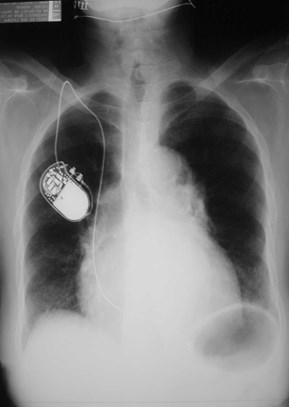
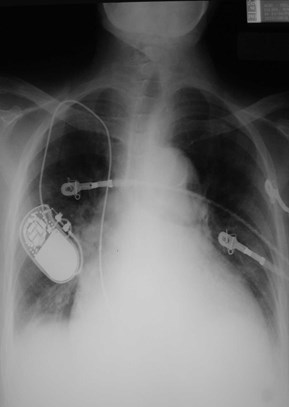
Radiographic technique:
Is it really different?
Changing technique can makedisease look better or worse.
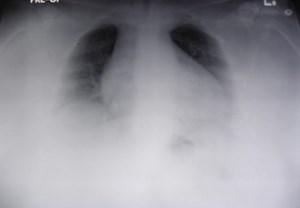

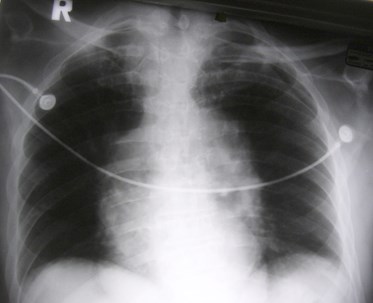
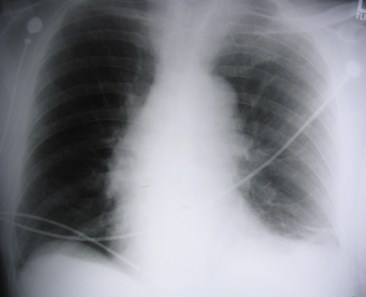
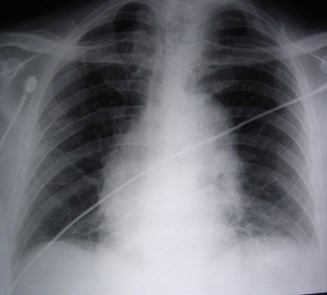
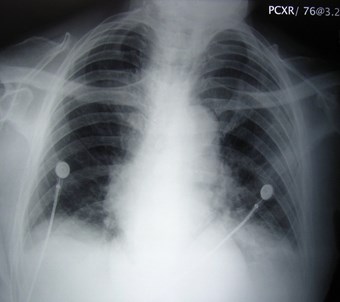
Is the heart large? Is themediastinum wide?
Same patient, 4 films within one month

Recognizing air space disease
•Alveolar spaces filled with…something.
•Radiologists’s report:
“consolidation”
“air space opacity”
“fluffy density”
“infiltrate”
•Nonspecific:
Atelectasis, pneumonia, bleeding, edema, tumor

The Silhouette Sign
•Indicates air space disease.
•Obscuration of a normally seenborder, e.g. diaphragm or heart.
•Opacity with sharp edge along afissure.

Localizing disease from thesilhouette sign
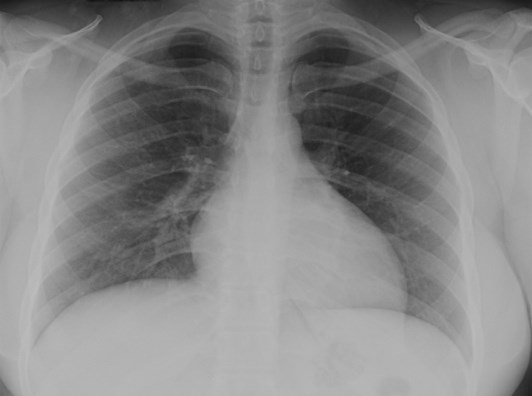
RLL
RML
LLL
Lingula
LLL

Localizing disease from thesilhouette sign

RUL
RML
UL
LL
RML orlingula

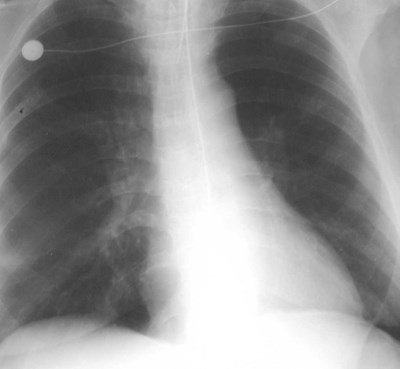
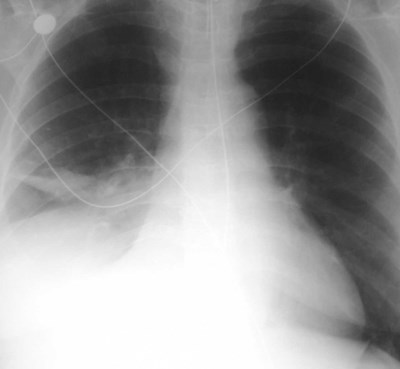
16 hours later
What happened here?What happened here?

Lobar Atelectasis
•Best sign -- shift of a fissure
•Rapid development and clearance
•Air bronchograms if non-obstructive
•Secondary signs:
Mediastinal shift
Elevated diaphragm
Ribs closer together
Vague increased density

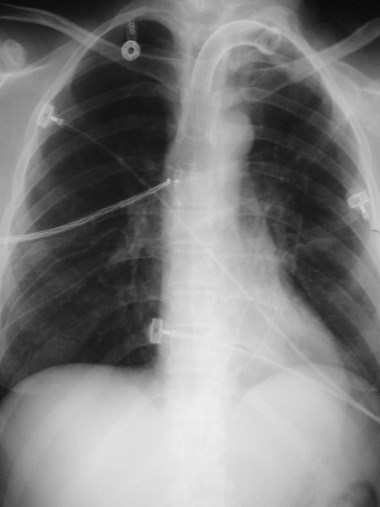
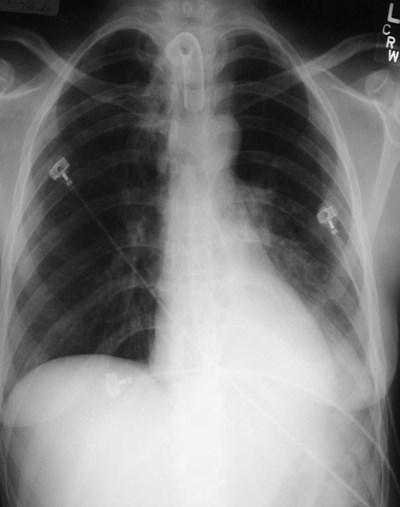
LLL Atx
Next day

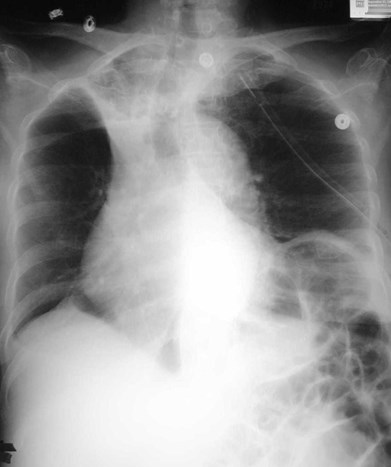
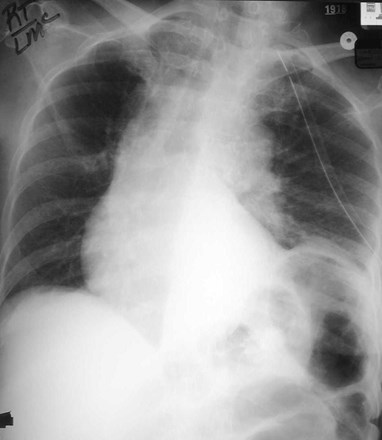
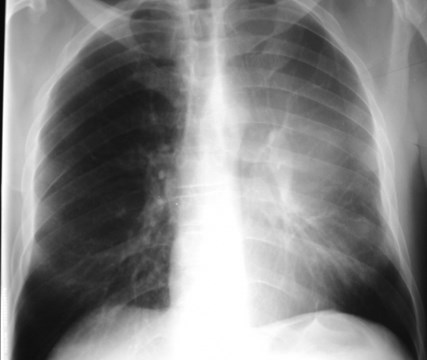
RUL Atx

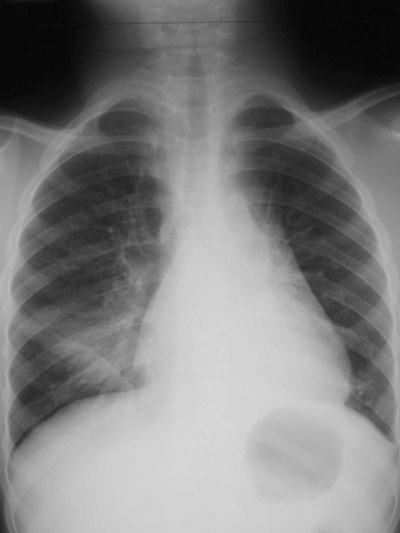
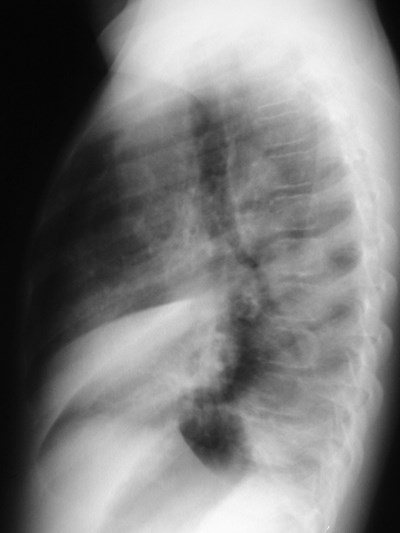
RML Atx

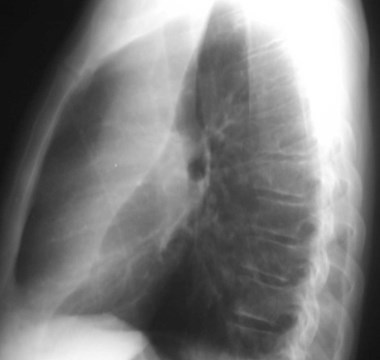
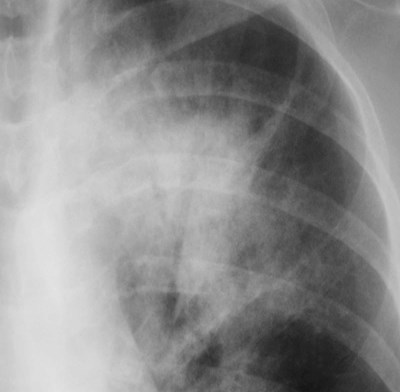
LUL Atx

Pneumonia
•Signs
Air bronchogram
Silhouette - “positive” or “negative”
Dense hilum
“Spine” sign
•All are signs of any air space process
•Dx of pneumonia depends on appropriateclinical scenario.

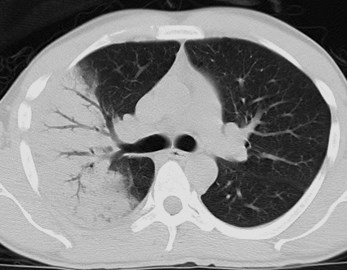
Air bronchogram sign
Pseudomonaspneumonia
Lung cancer

Air bronchograms—CT
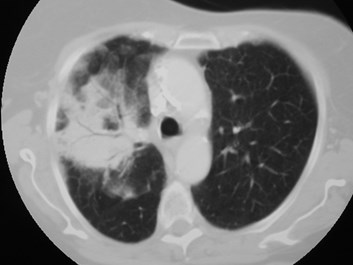
Pneumonia
Lung cancer

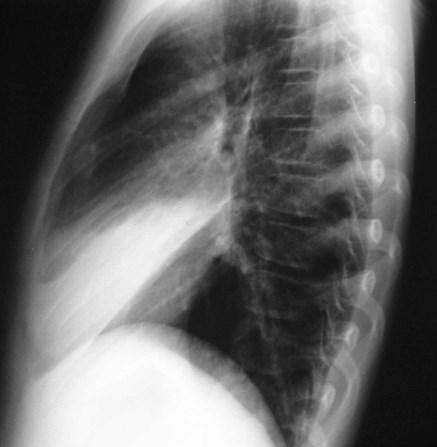
Right middle lobe

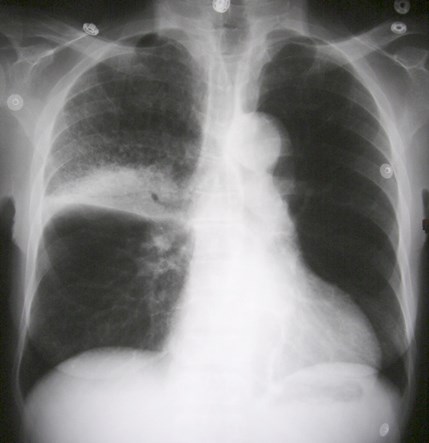
Right upper lobe

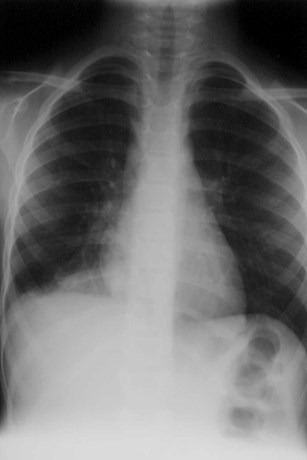
Right lower lobe
Posterior diaphragm silhouetted

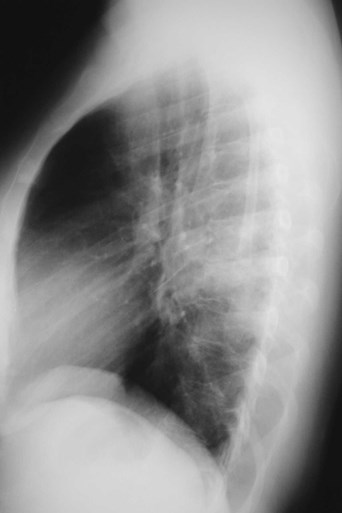
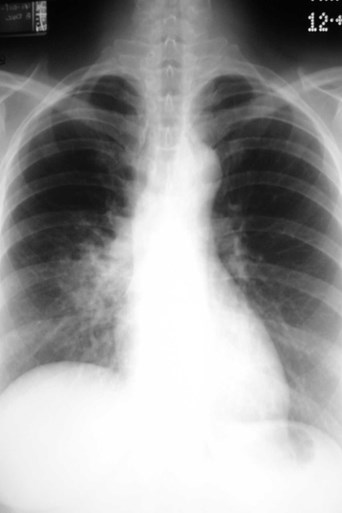
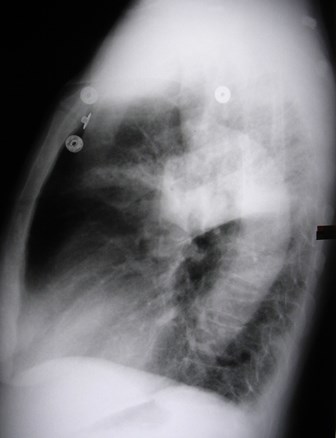
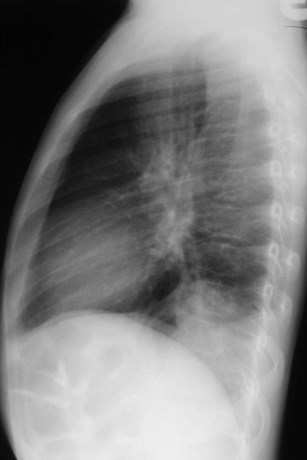
Dense hilum, spine sign

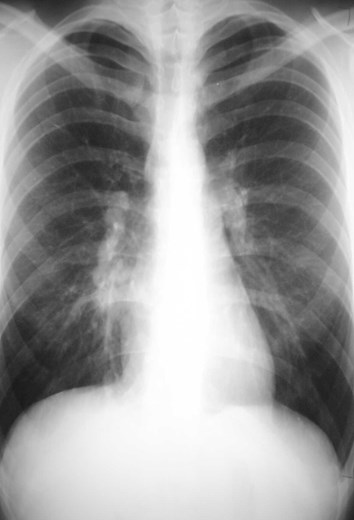
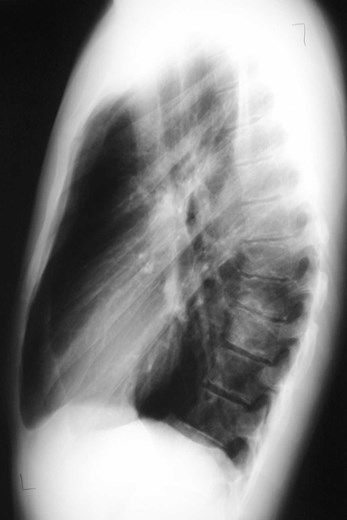
Dense hilum, spine sign again

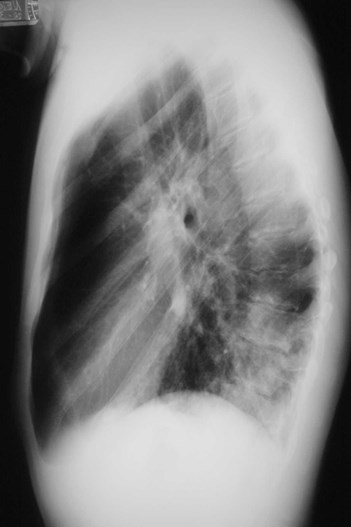
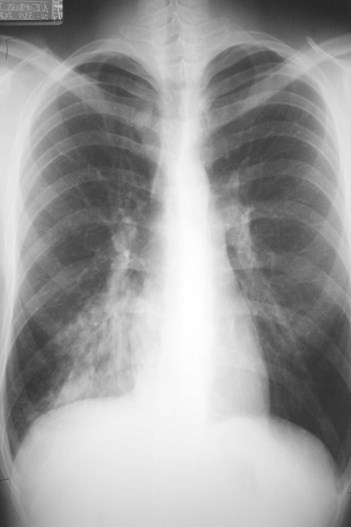
Four days later

Final Exam

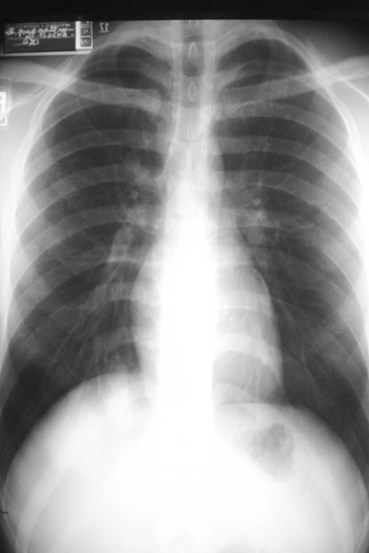
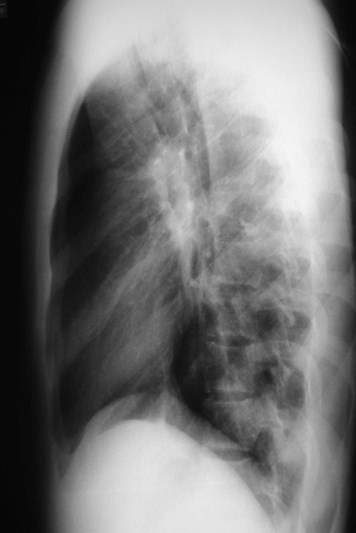
21 y.o. with fever and cough

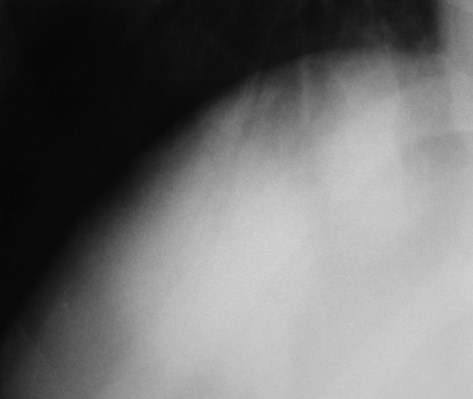

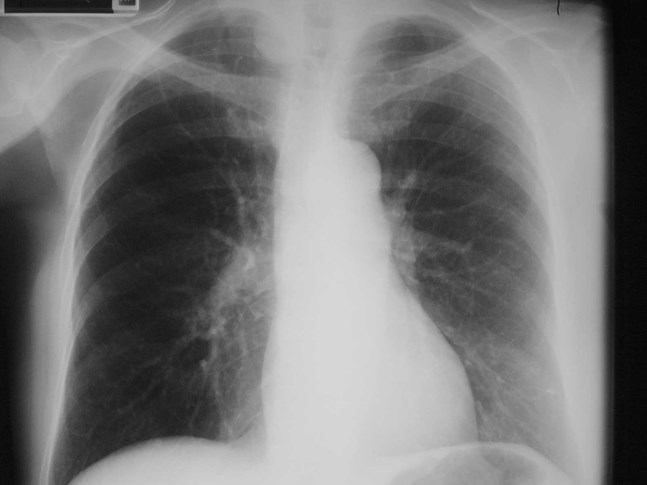
Hyperlucenthemithorax: why?

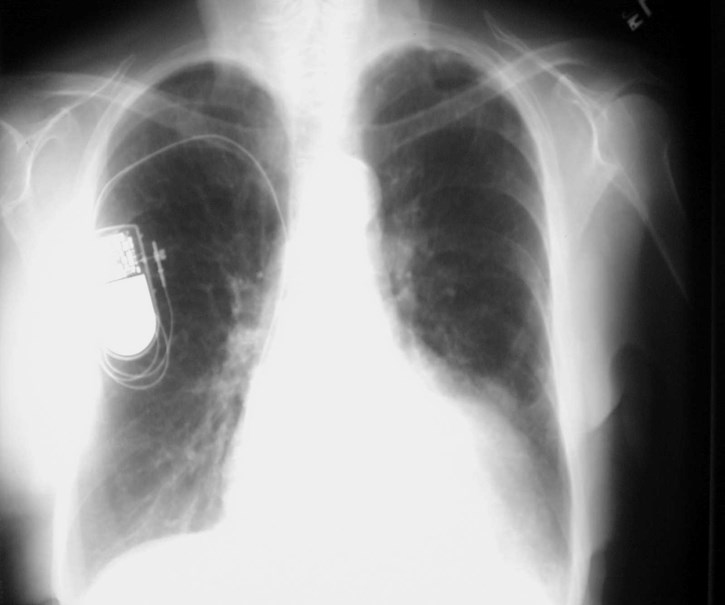
Did you notice the mass?

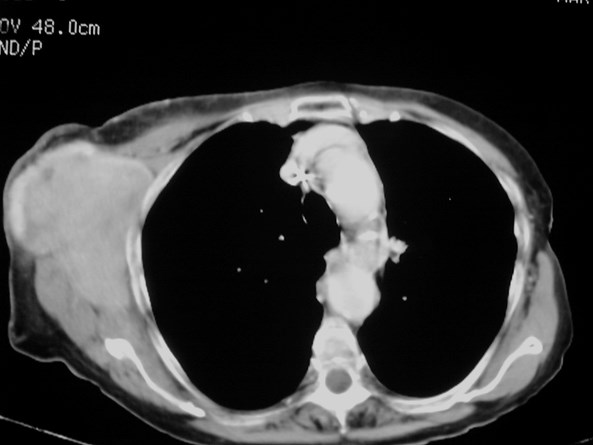
Lymphoma

Take home message #1
It’s a chest x-ray,
not a lung x-ray.

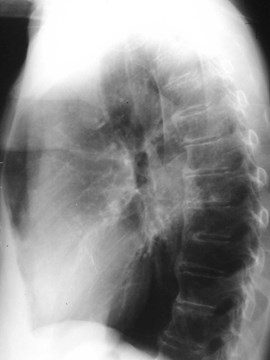
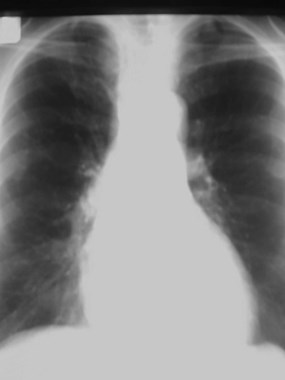
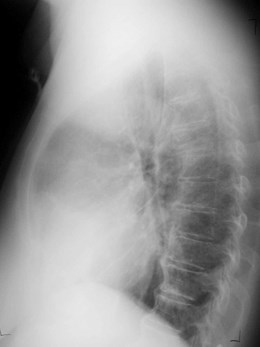
6 cm lung mass missed. How?
2 years ago

Take home message #2
Old films are your friend!

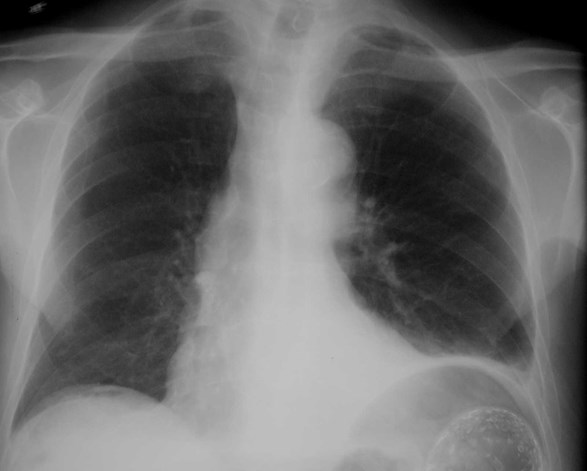
Elderly man with hypotension

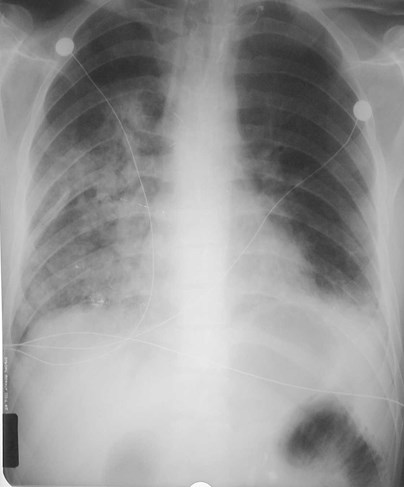
Suddenly septic

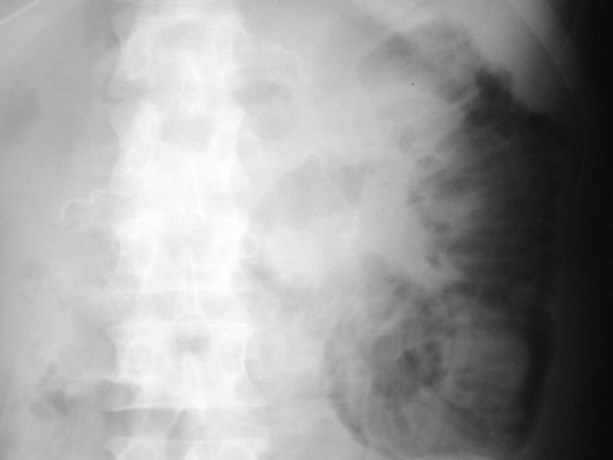
Pneumatosis of small bowel

Take home message #3
The patient pays forthe whole film!

Questions

All are kinds of air spacedisease except
•Hemorrhage
•Pneumonia
•Tumor
•Sarcoidosis
•Atelectasis

The most specific sign ofatelectasis is:
•Obscuration of a diaphragm
•Shift of a fissure
•Air bronchograms
•Density over the spine
•Mediastinal shift

This can make the heart looklarger than it is:
•Lordotic positioning
•AP positioning
•Expiratory film
•Supine positioning
•All of the above


Reading